 通过xml文件加载BeanDefinition
通过xml文件加载BeanDefinition
# 通过xml文件加载BeanDefinition
# BeanDefinition的资源定位过程
# ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
该方式使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来创建Spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类的UML图如下:
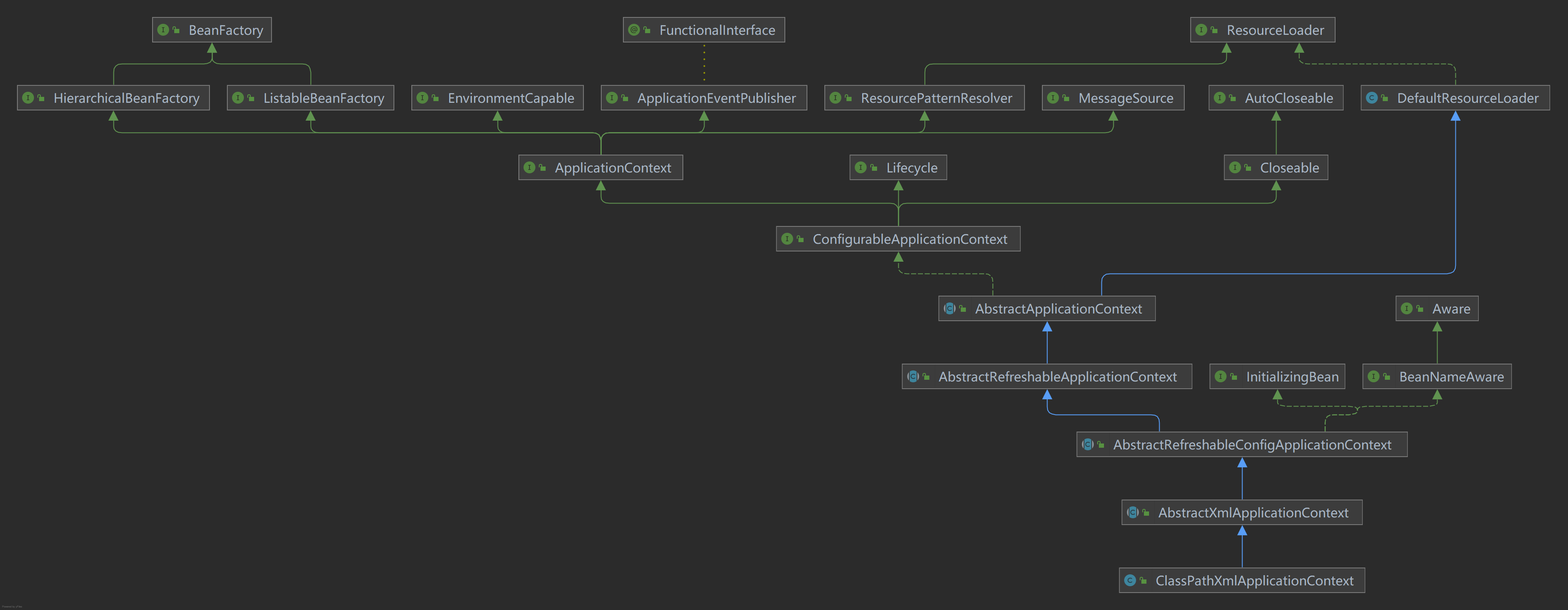
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext继承了AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh在刷新容器的第二步AbstractApplicationContext#obtainFreshBeanFactory方法中 会执行到AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
loadBeanDefinitions既是加载BeanDefinition的方法
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
将环境配置封装到XmlBeanDefinitionReader,委托该类进行加载
# XmlBeanDefinitionReader
XmlBeanDefinitionReader继承AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions的模板方法
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
//根据配置文件路径获取配置资源
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
return count;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
resourceLoader是上一步被封装到XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,从UML图中可以看到它间接实现了ResourcePatternResolver,所以走第一个if分支
最终还会调用到XmlBeanDefinitionReader#doLoadBeanDefinitions
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//读取配置资源,生成文档类
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//从文档类注册BeanDefinition
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
return count;
}
// ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
XmlBeanDefinitionReader#registerBeanDefinitions
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
2
3
4
5
6
这里又委托给DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader进行解析注册
# DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
//解析profile,支持多个
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
// We cannot use Profiles.of(...) since profile expressions are not supported
// in XML config. See SPR-12458 for details.
//如果profile不符合则不解析
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
preProcessXml和postProcessXml是留给子类实现的前置处理和后置处理,在DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader中是空实现
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
//默认标签解析
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
//默认标签解析
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
//自定义标签解析
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
//自定义标签解析
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
到这里Spring完成了对于配置文件的资源定位,以及dom解析生成BeanDefinition。对于具体的默认标签解析 (opens new window)和自定义标签解析 (opens new window)后面再详细记录。
